Objectif :
La
lecture de données à partir du clavier n'étant pas
aussi simple en Java qu'en Delphi (il n'y a pas d'instruction Readln
dédiée), nous fournissons une classe dénommée
Readln qui sera utilisée dans les programmes du package. Elle est
réutilisable dans tout programme personnel.
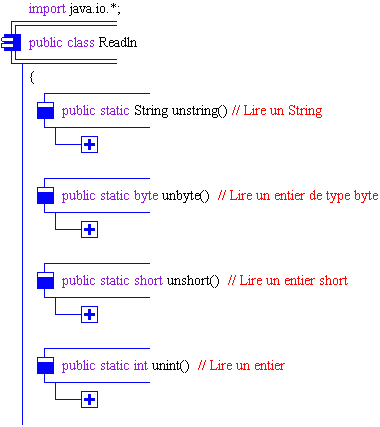
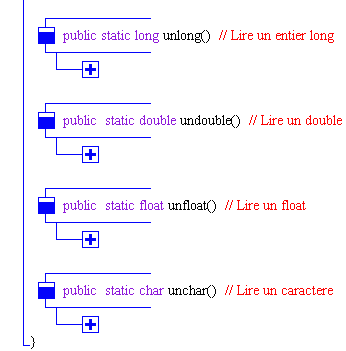
Image en diagrammes structurés JGrasp-Like de la classe
Readln

informations sur les diagrammes
Classe Readln :

Les méthodes de la classe
Readln :
Exemple d'utilisation de la classe
Readln :
( lecture au clavier d'une donnée
et affichage sur la console )
public class LireEcrire {
public static void main(String
[] argument) {
String Str;
int age;
long Distance;
System.out.print("Entrez
une chaîne : ");
Str
= Readln.unstring( );
System.out.println("Chaîne
entrée : "+Str);
System.out.print("Entrez
un int: ");
age
= Readln.unint( );
System.out.println("Valeur
de l'int entré : "+age);
System.out.print("Entrez
un long : ");
Distance
= Readln.unlong( );
System.out.println("Valeur
du long entré : "+Distance);
}
} |
Remonter 
Implantation en Java de la classe
Readln :
import java.io.*;
public class Readln
{
public static
String unstring() // Lire un String
{
String Strloc =
new String(); //<=> Strloc ="";
char Carlu='\0';
try {
while ((Carlu=(char) System.in.read()) !='\n')
if (Carlu != '\r') Strloc = Strloc+Carlu;
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Erreur de saisie");
System.exit(0);
}
return Strloc;
} //
fin de unstring() |
public static
byte unbyte() // Lire un entier de type
byte
{
byte b=0;
try {
b=Byte.parseByte(unstring());
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Entier byte incorrect");
System.exit(0);
}
return b ;
} //
fin de unbyte() |
public static
short unshort() // Lire un entier short
{
short s=0;
try {
s=Short.parseShort(unstring());
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Entier short incorrect");
System.exit(0);
}
return s ;
} //
fin de unshort() |
public static
int unint() // Lire un entier
{
int i=0;
long loc=unlong();//
un int est un long particulier
i=(int)loc;
return i ;
} //
fin de unint() |
public static
long unlong() // Lire un entier long
{
long L=0;
try {
L=Integer.parseInt(unstring());
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Entier long incorrect");
System.exit(0);
}
return L ;
} //
fin de unlong() |
public
static double undouble() // Lire un
double
{
double D=0.0; //
type réel par défaut de Java
try {
D=Double.valueOf(unstring()).doubleValue();
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Réel double incorrect");
System.exit(0);
}
return D ;
} //
fin de undouble() |
public
static float unfloat() // Lire un float
{
float F=0.0f; //
sinon double par défaut
try {
F=Double.valueOf(unstring()).floatValue();
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Format numérique incorrect");
System.exit(0);
}
return F ;
} //
fin de unfloat() |
public
static char unchar() // Lire un caractere
{
String Strloc=unstring();//
un caractère est un string particulier
if (Strloc.length()==0)
return '\n';
else
return Strloc.charAt(0);// on ne prend que
le premier caractère
} //
fin de unchar() |
} |
Remonter 





